What is GMP?
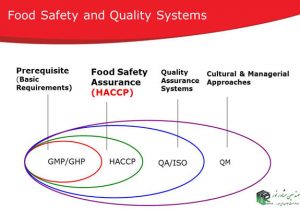
All consumers have the right to expect healthy and good quality food. Uncertainty of food safety can lead to the failure of food business. Safety systems / Quality management and food quality assurance throughout the supply chain, ensuring that food businesses can keep food safe. This set of preventive controls may include good agricultural systems (GAP), good manufacturing practice (GMP), good hygiene practices (GHP), and hazard analysis and critical control points (HACCP).

Good manufacturing practice (GMP) is a system to ensure the continuous production and control of products in accordance with quality standards.
In fact, GMP is a system that ensures that manufactured products such as food, cosmetics, and pharmaceuticals are continuously produced and controlled in accordance with established quality standards.
GMPs examine and cover all aspects of the manufacturing process to prevent potential hazards to products.
Implementing GMP can help reduce losses and protect both the company and the consumer from negative food safety events.

GMP covers all aspects of production from raw materials and equipment to training and personal hygiene of employees. Detailed written procedures are necessary for any process that can affect the quality of the final product. Systems must be in place to provide documented proof that the correct steps are in place at each stage of the manufacturing process – whenever a product is manufactured.
What are GMP regulations?
GMP regulations are mandated by national governments to regulate production, verify and validate manufactured products and ensure they are effective and safe for distribution on the market. For example, in the United States, GMP is enforced by the US FDA through Current Good Manufacturing Practices (CGMP), which covers a wide range of industries such as cosmetics, food, medical devices, and prescription drugs. The FDA conducts facility inspections to assess a manufacturing company’s compliance with CGMP regulations.
The quality of manufactured products is very important. Because it can bring risks to the health of consumers and even the environment. Improper hygiene, contamination at every stage of production, are some examples of how a manufactured product that does not follow GMP regulations can have fatal consequences for consumers.
What are GMP guidelines?
GMP guidelines are a set of principles that help manufacturers implement an effective manufacturing process and ensure that quality is maintained in the organization and related processes. GMP guidelines are typically flexible, countries have their own laws to comply with GMP guidelines and principles. But almost all regulations are derived from basic concepts and guidelines.
In general, in a production unit, the parts that fall under GMP rules are:
– Building
– Equipment
– Personnel
– Tests of raw materials
– production control
– quality control
– Testing of packaging materials
– Final product tests
– Documents and documents
– samples
– Dealing with complaints
And …
Basic principles of GMP
- Manufacturing facilities must maintain a sanitary production area, including laboratories and warehouses.
- To prevent cross-contamination of products, the design of production facilities, working principles and environmental conditions must be controlled.
- Manufacturing processes must be clearly defined, validated and controlled to ensure compliance with specifications.
- Instructions and procedures should be written in clear language (good documentation practices).
- Operators must be trained to produce and control products according to documented and approved methods.
- Records must be kept during manufacturing and quality control, and this shows that all the steps required by the defined guidelines have been carried out as per the definition and that the specified quality characteristics of the products have also been met. Deviations are investigated and documented.
- The work process must remain in control throughout the product life cycle and improvements made as necessary.
- Production records (including distribution) are maintained in an understandable and accessible format that can trace the complete history of a batch.
- A system must be in place to recall any batch of sales or supplies. Complaints related to the products offered in the market should be investigated. The causes of quality defects should be investigated and appropriate measures should be taken in relation to defective products and to prevent recurrence.
Who issues the GMP certificate?
GMP certificates are issued by the Food and Drug Organization or legal entities under the supervision of the above organization. In Iran, ISO certification centers also issue GMP certificates.
GMP certification process
After companies have developed and developed their internal system, they contact the government agency responsible for GMP certification. For example, in the United States, the Food and Drug Administration (FDA) is responsible for this.
Once the Ministry of Health receives the request, its GMP experts inspect all aspects of the company to ensure compliance with the standard. The inspection will include materials used, storage and packaging conditions, research and development, quality control, spaces and layout, etc.
It is important to note that inspections are different from audits, as inspections involve the demonstration of certain tests to ensure compliance. GMP inspection is much more complex than ISO9001 standard audit, because GMP includes detailed technical requirements that require more complex methods than ISO9001 standard.
According to the GMP inspection results, a GMP certificate will be issued to the company. If the company is unable to meet the GMP requirements, the inspectors will give the company another chance to meet the requirements and receive a GMP certificate after meeting these requirements.
What are GMP standards?
GMP standards are established to increase the safety of manufactured products, especially pharmaceutical goods, and to ensure the highest possible quality for consumers. Compliance with GMP standards not only positively affects the reputation of manufacturing companies, but also reduces negative consumer reports.
GMP standards are not guidelines for how products should be manufactured. Rather, they are a set of performance-based requirements that must be met during production. When a company is setting up its quality program and manufacturing process, there may be many ways to meet GMP requirements. It is the responsibility of the company to determine the most effective and efficient quality process.
Below are steps you can take to maintain GMP standards:
-
Quality team
Have a team of skilled workers focused on improving current manufacturing methods and GMP compliance. Members conduct performance evaluations to identify problems and develop appropriate corrective actions. Part of the team’s responsibility will be to conduct planned monitoring of tools, equipment, processes and employee skills.
-
Validation
Validation is documented practice to demonstrate that tools, processes, and activities are used or performed regularly. This is done to check if performance meets expectations. GMP can include items that must be approved.
-
Surprise audits
From time to time, a surprise audit can help to better understand the events. Identify the root causes of non-compliance and take action before it becomes a bigger issue.
-
Compliance training
Providing compliance training to employees is the best way to ensure compliance with GMP standards. Help staff to better understand GMP and continuously improve existing operations or systems to ensure standards are consistent with GMP. All employees should receive training in record keeping and proper use of equipment to minimize errors and maintain compliance.
What is GHP?
Improving health management in the food supply chain is very important.
The general principles of food hygiene are applied through the implementation of good hygiene practices (GHP) to GAP and GMP. GHP recommends a HACCP-based approach to reduce risks.
GHP compliance covers minimum hygiene measures for industries involved in food preparation (such as hotels and restaurants), to ensure food is safe and fit for human consumption. GHP is a necessary foundation for the implementation of other food safety management practices such as GMP, HACCP and ISO22000 standard.
GHP is applied to the entire food chain (including primary production to the final consumer), to ensure that food is healthy and suitable for consumption.
Compliance with GHP highlights areas of concern and potential problems for improving food safety standards.
What is a GMP audit checklist?
The Good Manufacturing Practices (GMP) audit checklist is a tool used by manufacturers to ensure the quality of food, pharmaceutical, medical, and cosmetic products and compliance with manufacturing standards. Conducting regular GMP audits protects businesses from product safety issues, product recalls, and legal and regulatory issues.
How to prepare for a GMP audit?
- Review the GMP audit scope
- Communicate the audit schedule to your team.
- Ensure that the plan is communicated to all site personnel, especially those whose areas will be audited.
- Clearly list the systems and products under review.
- List specific dates for each audit.
- Determine which standards are covered in a GMP audit.
- Be sure that you are familiar with the exact standards and policies related to their interpretation and application. Know your documents and prepare them ahead of time.
- Before the audit, make sure your team has reviewed any documents an auditor might request. Ensure that all documents are available and that all published documents are “version controlled” and up to date.
Noor Management Consultants Group is always waiting to receive your opinions, criticisms, suggestions and questions
Contact us if you need a free consultation
02188761795
02188764867




No views