Issue: Customer relationship management, clustering (customer segmentation)
RFM analysis for successful customer segmentation – Part I
the writer :
Mr. Engineer Behnam Behzadi Far / Respected manager of relationship with customers of Mustafavi Saffron brand

RFM Monetary Recency (Frequency) Analysis is a proven model for behavior-based customer segmentation. In this method, customers are divided based on the history of their transactions and purchases, how many times and how much they have bought recently. RFM helps to segment customers into different categories or clusters. For example, customers who are more likely to respond to advertisements or customers who are considered for marketing processes in the future.
Combination of three components
Evaluating customers based on only one parameter is not a sufficient and appropriate solution. For example, you can say that the people who spend the most are your best customers. In this matter, most of us agree and think alike. But what if they only bought once, or they bought a product a long time ago, or they don’t want to buy your product at all? So can they still be considered the best customers? Probably not.
Judging customer value from only one aspect will give you an inaccurate account of the customer and their lifetime value.
As you know, RFM analysis is a useful method to find your best customers, understand their behavior and then implement targeted marketing programs to increase sales, satisfaction and customer lifetime value. In this method, the RFM model combines three different customer characteristics to rank customers.
If they shop in the recent past, they get more points. If they shop multiple times, they get higher points. And if they spend more, they get more points. You can easily combine these three scores to create the RFM score.
Finally, you can divide your customer database into different groups based on this score of delay, frequency and bridge turnover.
Customer segmentation with RFM model
Through RFM analysis you can create different types of customer segmentation, here we suggest 11 segments. Think about what percentage of your current customers are in each of these segments, and
Evaluate how effective the proposed marketing measures can be for your business.
| Row | Customer type | Activity | Applicable tips |
| 1 | Champion | They have bought recently, they buy often and spend the most. | Reward them, they can be the fastest buyers of your products and promote your brand. |
| 2 | Loyal customer | They often spend good money with us. They respond to advertisements. | Sell your valuable products, engage them, make them yours. |
| 3 | Potentially loyal | Recent customers, however, have spent a lot and bought more than once. | Offer membership/loyalty program, offer other products. |
| 4 | Recent customer | They have bought recently, but they do not buy regularly. | Offer ongoing support, give them a sense of early success, start building a relationship. |
| 5 | hopeful | They bought recently but did not spend much. | Build your brand awareness, offer free trials of your product or service. |
| 6 | need attention | Values beyond the value of delay, frequency and cost. They may not have shopped recently. | Offer limited offers, offer based on previous purchases. Reactivate them. |
| 7 | declining | Values are lower than the value of delay, frequency and cost. If you don’t pay attention to them, you will miss them. | Share valuable resources, offer popular or new products at a discount, reconnect with them. |
| 8 | in danger | They spent a lot of money and bought often, but a long time ago. You need to return them. | Send personalized emails, offer amazing offers, and provide helpful resources to reconnect. |
| 9 | They should not be missed | They have had the largest and most stable purchases, but they have not been open for purchases for a long time. | Win them back through product refreshes or new products, don’t lose them to the competition, talk to them. |
| 10 | Hibernate | Their last purchase was a long time ago, the number of orders and their cost is very low. | Offer them other related products with special discounts. Create brand value. |
| 11 | lost | They have the lowest yield, frequency and monetary points. | By creating extensive and quality campaigns, rekindle the passion and interest in the buyer, otherwise you have to kill the customer. |
Segmentation of customers based on RFM Easily answer this questionValat Answers for your business
- Who are my best customers?
- Which customers are on the verge of dissatisfaction?
- Who has the ability to become a profitable customer?
- Who are the lost customers you don’t need to pay much attention to?
- Which customers should you keep?
- Who are your loyal customers?
- Which customer groups are most likely to respond to your current campaign?
Score calculations RFM in a simple word
If you don’t know how to calculate RFM points according to the data in your customer database, here we explain how to do the calculations in simple language. Remember we need all the details of our customers’ information. for example:
- Customer ID / Email / Name etc.: To identify them
- Recency (R) – the date or days of the last purchase: How many days ago was their last purchase? To calculate shelf life, subtract the most recent purchase date from today. 1 day ago? 14 days ago? 500 days ago?
- Frequency (F) purchase frequency – total number of transactions (purchases): How many times has the customer bought from your store? For example, if someone makes 10 orders in a period, his frequency is 10.
- Monetary (M) purchase cost – total purchase cost: How many tomans (or any monetary unit) has this customer spent? Again, limited to the last two years – or the entire period since the first purchase. To get the value of M, it is enough to add up the money of all transactions.
Let’s do RFM analysis with an example
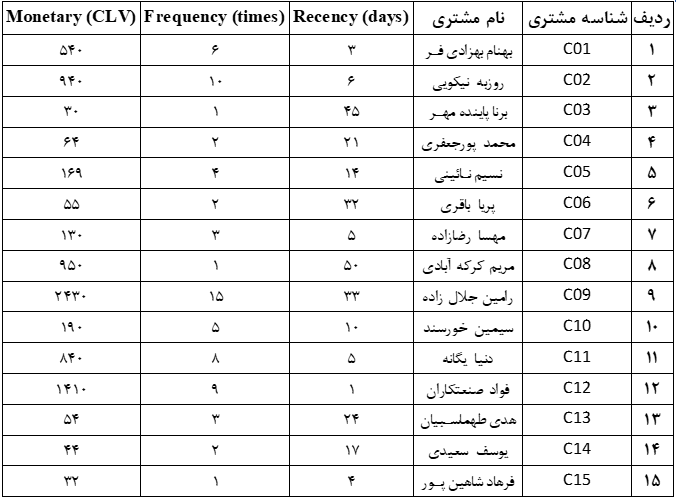
For example, consider customer number 1 Behnam Behzadifar, his last order was 3 days ago and he has had a total of 6 orders worth 540 thousand tomans till date.
Apply the RFM formula
When we collect RFM item values from customers’ purchase history, we assign a score from one to five to each of the R, F, and M values for each customer separately. A score of five is the best (highest) value and a score of one is the worst (lowest) value. The final RFM score is simply calculated by combining the unique RFM numbers for each customer.
Remember, values RFM and privileges RFM The two issues are different. Value real amount R / F / M For each customer, while Score (score) based on the value of one Number from 1 to 5 Is.
Let’s take a closer look at the table below. To calculate the score, we first sort the values in descending order (highest to lowest). Since we have 15 customers and five points, we assign 5 to the first three records, four to the next three, and so on. For the overall RFM score, we simply combine the R, F, and M in the customer’s score to create a three-digit number.
Notable point: Recent purchases are evaluated better and hence are awarded a higher score.
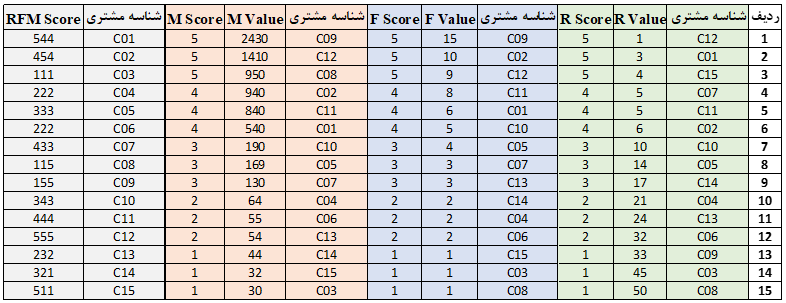
Therefore, it can be easily concluded that customers who have bought recently are frequent buyers and spend a lot of money, i.e. they have a score of 555, which is assigned a value of 5 for F, R and M. They are your best customers. In this example, Fouad Sanatkaran is the best customer, not Ramin Jalalzadeh, who even had the highest purchase volume.
Makes sense, right? Now let me explain why we made groups of three for each score. Below I will list the methods that will make your work easier!
How to calculate the RFM score on a scale of 1-5?
Different businesses may use different methods of RFM formulas to rank RFM values on a scale of 1 to 5. But here we mention two common methods.
First method: Fixed ranges
Let’s go with an example.
If someone made a purchase in the last 24 hours, give them a 5. In the last 3 days, give him a rating of 4. Assign 3 if they bought in the current month, 2 for purchases in the last six months, and 1 for everyone else. As you can see, we have set a range for each of our scores. Domain thresholds are based on the nature of the business. In the same way, set the ranges for F and M as well.
This scoring method More To Individual businesses It depends – because they decide a wide range for R، F And F Consider it ideal.
But this fixed period/amplitude calculation model for calculating RFM scores also has challenges. As the business grows, grade ranges may need to be adjusted frequently. If you have a business with frequent payments, but with different payment terms, monthly, yearly, etc., the calculations will be wrong.
The second method: pentagonal – According to Value existing, make a pentagon
- pentagonal: Divide a circle into 5 equal parts, each part having an angle of 72 degrees.
Let’s remember our school days. There was a term, calculation based on 100, which in mathematics is called Percentile. A simple definition of Percentile is the percentage of values that are observed in or under a particular observation. Here’s a chart from MathIsFun.com that explains it clearly:
What are Percentiles and Quintiles?
Quintiles are like Percentiles, but instead of dividing the data into 100 parts, we divide them into 5 equal parts. Quintiles will be easier to understand if you understand the concept of Percentiles. If we create five equal intervals of Percentiles, the 18th Percentiles score will be in the 0-20 range, which will be the first Quintiles. Percentiles 81 will be in the 80-100 range and hence will be the fifth quintile. This mathematical method is a bit complicated, but it solves many problems in the first method. Quintiles works for any industry and business because when domains are selected from the data itself, it distributes customers evenly and does not cross over.
Our suggested method for calculating points RFM using Quintiles Is.
Summary of calculations RFM
Collect your customer information and data, rate the R, F and M values from 1-5. Using the Quintiles method works best because it works for all businesses and adjusts to your data.
Stay with us in the next part to talk more about the RFM method, which is simple yet very practical and can transform your business.





No views